Earth observation satellites
Earth observation satellites provide data on oceans, ice, land environments, and the atmosphere. They are useful for monitoring and protecting our environment and planet and for helping us better understand them. They help us manage our resources and ensure the safety of Canadians. Experts use satellite images to support humanitarian efforts and sustainable development around the world.
What's new?
The various Earth observation satellites
Active Canadian satellites
-
RADARSAT Constellation Mission
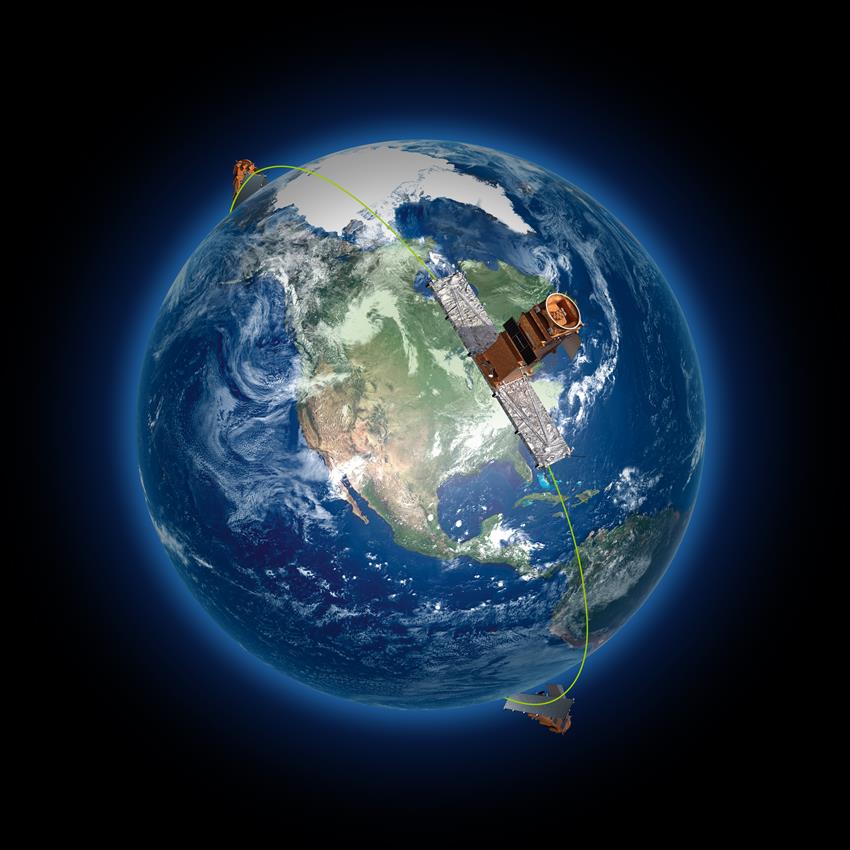

Characteristics: Canadian satellites, active
The RADARSAT Constellation Mission was launched on . It is Canada's third generation of Earth observation satellites. Three identical satellites work together. They bring solutions to key challenges for:
- maritime surveillance
- disaster management
- ecosystem monitoring
-
RADARSAT-2
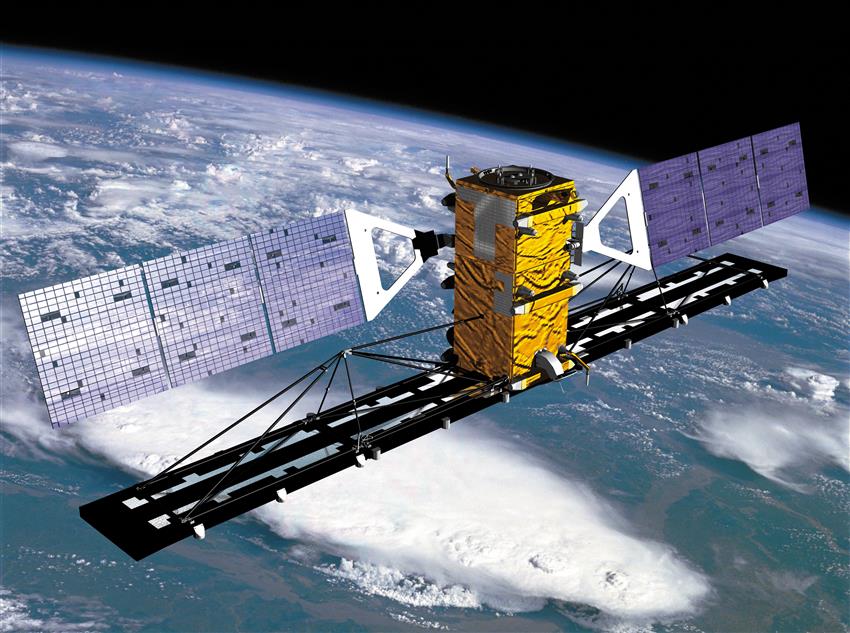

Characteristics: Canadian satellite, active
MDA's commercial radar satellite was launched in . It facilitates:
- ice, marine, and environmental monitoring
- disaster and resource management
-
SCISAT

Characteristics: Canadian satellite, active
SCISAT was launched on . It is used to monitor the ozone layer. In particular, it enables observation of the changes occurring over Canada and the Arctic.
It passes over:
- polar regions
- tropical zones
- mid-latitude locations
Canadian satellites in development
-
HAWC

Characteristics: Canadian satellite mission in development
HAWC will launch in . It will provide critical data to support extreme weather prediction, climate modelling, and monitoring of disasters. consists of three innovative Canadian instruments and a Canadian satellite that will be part of the international NASA-led Atmosphere Observing System (AOS).
It will make it possible to:
- Observe mid-to high-altitude aerosol particles.
- Measure water vapour in the upper reaches of the lower atmosphere. Water vapour is a powerful greenhouse gas.
- Observe water vapour and ice cloud properties. It will also measure the energy that the atmosphere radiates to space.
-
WildFireSat
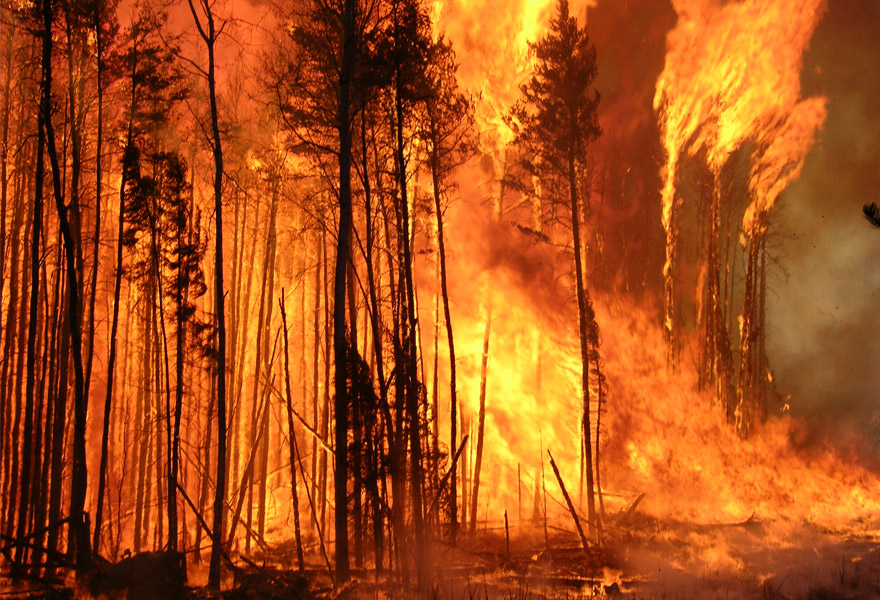

Characteristics: Canadian satellite, in development
WildFireSat is scheduled to launch in . It is intended to support active wildfire monitoring and management in Canada.
It will make it possible to:
- anticipate wildfire behaviour and determine which wildfires are high risk and should therefore be prioritized
- obtain more accurate data on smoke and air quality
International satellites to which Canada has contributed
-
CloudSat

Characteristics: Canadian elements, active
NASA's CloudSat satellite was launched on , and is part of a constellation of satellites. It helps us better understand clouds and their effect on climate and weather. As part of a first-ever comprehensive three-dimensional study of clouds, it gathers data on:
- their structure
- their occurrence
- their volume
-
Odin

Characteristics: Canadian instrument, active
The Swedish satellite Odin was launched on . Since then, it has been collecting data for studying climate and atmospheric changes. Canada's OSIRIS instrument measures atmospheric composition, focusing mainly on the upper atmosphere. It provides data on:
- ozone depletion
- concentrations of aerosols and nitrogen dioxide
-
SMAP
Characteristics: Canadian elements, active
NASA's orbiting laboratory/satellite, SMAP, was launched on . It is used to map soil moisture and freeze/thaw state. It helps:
- improve climate and weather forecasts
- monitor droughts and better predict flooding
-
SMOS

Characteristics: Canadian elements, active
The European Space Agency's SMOS was launched on . It is the first satellite designed to both map sea surface salinity and monitor soil moisture. Its secondary objective is to map snow- and ice-covered regions.
The data provided helps us better understand:
- how water moves across the planet
- how our climate systems work
-
SWOT
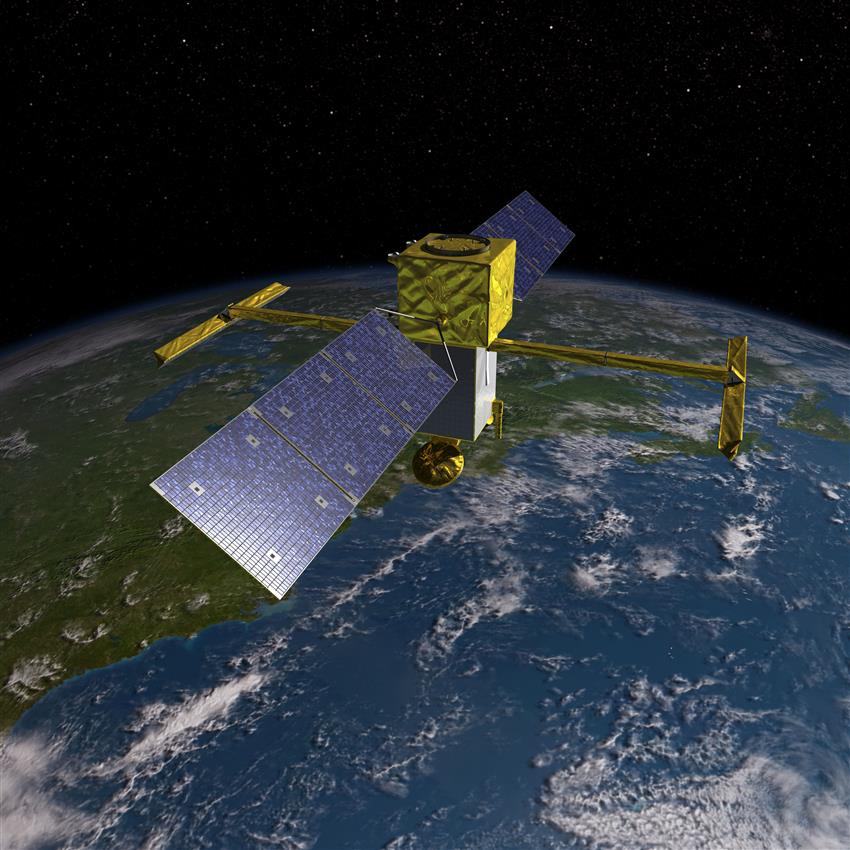

Characteristics: Canadian elements, in development
The SWOT mission led by NASA and the Centre national d'études spatiales (France's space agency) is scheduled to launch in . It will provide detailed information on water, one of Earth's most precious resources.
It will be able to:
- survey 90% of Earth's surface water
- observe the details of the ocean surface topography
- measure how lakes, rivers, reservoirs, and oceans are changing
-
Terra
Characteristics: Canadian instrument, active
NASA's Terra satellite was launched on . It carries five instruments that observe Earth's atmosphere, ocean, land, snow and ice, and energy budget. The Canadian instrument MOPITT continuously scans Earth's atmosphere to measure carbon monoxide (concentrations, distribution, transport).
It is used to:
- forecast the long-term effects of pollution
- orient the assessment and implementation of short-term pollution controls
Inactive Canadian satellites and instruments
-
Envisat

Characteristics: Canadian elements, inactive
Launched on , the Envisat satellite, led by the European Space Agency, was the largest Earth observation satellite ever built at the time. It had 10 instruments.
Envisat's data helped:
- understand the components of the Earth system (e.g., oceans, continents, flora, fauna, layers of the atmosphere)
- make informed decisions about how to protect the environment
-
RADARSAT-1

Characteristics: Canadian satellite, inactive
Launched on , RADARSAT-1 was a sophisticated Earth observation satellite developed by Canada. It was used to monitor environmental changes and Earth's natural resources. It is in part thanks to RADARSAT-1 that Canada has become a world leader in the processing of satellite remote sensing data.
With its powerful synthetic aperture radar, RADARSAT-1 was able to produce images of Earth:
- day or night
- in all weather conditions
- through cloud cover, smoke, and fog

