About the Mobile Base System
Part of Canada's contribution to the International Space Station (ISS), the Mobile Base System (MBS) is a moveable work platform and a storage location. It can transport:
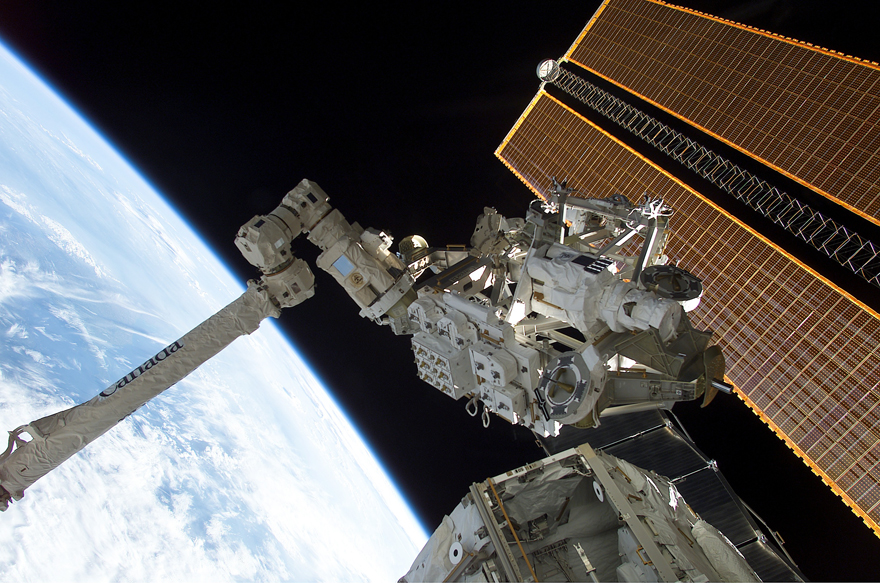
Canada's contribution to the International Space Station consists of cutting-edge robots Canadarm2 and Dextre, and the Mobile Base System, a transport and storage platform.
All three elements are essential for many maintenance tasks and regular operations.
How the Mobile Base works
Mounted on the Mobile Transporter rail car, the Mobile Base can glide along the main truss of the ISS. The MBS allows Canadarm2 and Dextre to access any of eight worksites that feature power connections for the Base and any of its attachments.
When the Mobile Transporter and Mobile Base need to move together along the truss, the Base and its attachments are powered down. When they are latched in place at a new worksite, they are powered up and work can begin.
Special features
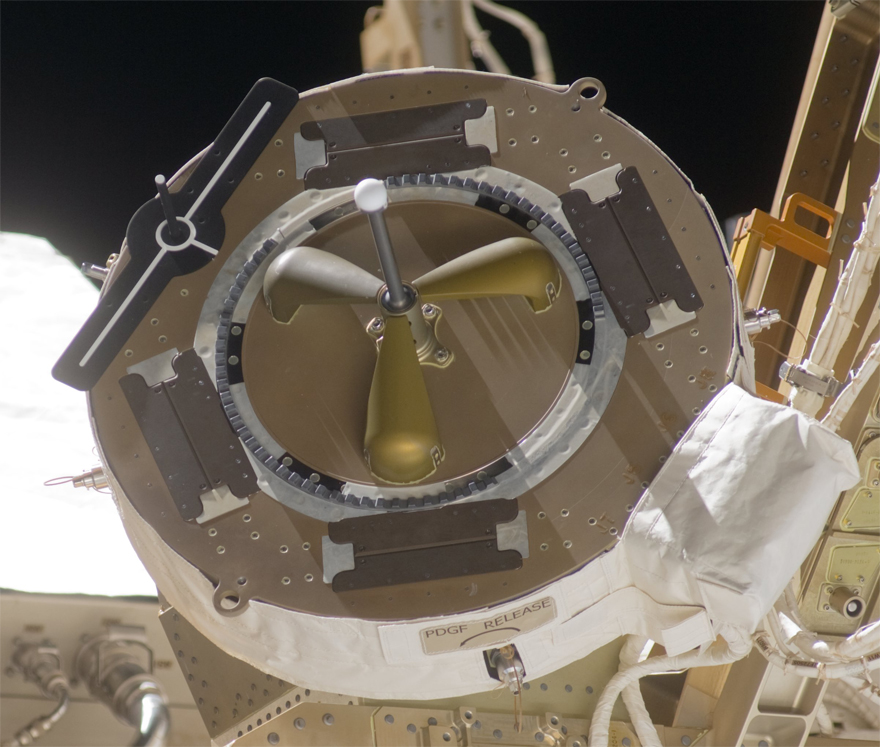
The Mobile Base has four power data grapple fixtures, the anchor points that allow Canadarm2 and Dextre to connect to the Base. These fixtures allow the robots to receive power, data, and video connections from the ISS.
Who controls the Mobile Base?
The Mobile Transporter, on which the MBS is mounted, is operated by the ground team at the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) headquarters and NASA.
Who built the Mobile Base?
The Mobile Base was built by MacDonald, Dettwiler and Associates, based in Brampton, Ontario. It was launched on board Space Shuttle Endeavour in .
Data sheet
| Dimensions | 5.7 m x 4.5 m x 2.9 m |
|---|---|
| Mass | 1,584 kg |
| Peak power (in operation) | 825 W |
| Minimum power (to remain functional) | 365 W |